Halfway through 2013, and the FCC’s pace of unlicensed broadcast enforcement shows no real change from 2012: 106 enforcement actions in all, targeting more than three dozen stations, with the majority of this activity wholly administrative in nature. Pirate stations who appear on the FCC’s radar can now expect a warning letter to arrive via certified mail 1-6 weeks after an initial visit. Ignore those, and the agency may start asking for money.
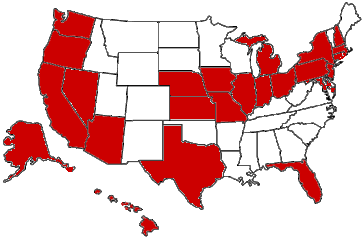 To date, the FCC has handed out $60,000 in Notices of Apparent Liability and $125,000 in actual forfeitures. However, not all of these penalties are new: in February, the FCC socked Whisler Fleurinor with a $25,000 fine for unlicensed operation in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. This is actually Fleurinor’s second go-round – he was first busted in 2010 and given a $20,000 forfeiture in 2011, which was later reduced to $500. It’s much the same story for Gary Feldman, who was first busted in 2004 for pirate broadcasting in Miami. He was caught again last year and fined $25,000 this year. Moreno’s 2004 forfeiture ($10,000) was never paid. Continue reading “Pirate-Hunting: FCC Plods While Local Scenes Bubble”
To date, the FCC has handed out $60,000 in Notices of Apparent Liability and $125,000 in actual forfeitures. However, not all of these penalties are new: in February, the FCC socked Whisler Fleurinor with a $25,000 fine for unlicensed operation in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. This is actually Fleurinor’s second go-round – he was first busted in 2010 and given a $20,000 forfeiture in 2011, which was later reduced to $500. It’s much the same story for Gary Feldman, who was first busted in 2004 for pirate broadcasting in Miami. He was caught again last year and fined $25,000 this year. Moreno’s 2004 forfeiture ($10,000) was never paid. Continue reading “Pirate-Hunting: FCC Plods While Local Scenes Bubble”
Category: Microradio
Boston Radio Pirate Runs for Mayor
The city of Boston, Massachusetts is gearing up for a mayoral election later this year, and among the folks throwing their hat into the ring is Charles Clemons.
A former Boston police and corrections officer, Clemons may be better known as the founder of Touch 106 FM, a microradio outlet busted by the FCC in 2007-08. Clemons received a $17,000 forfeiture for unlicensed broadcasting and refusing to allow FCC agents to inspect the station. Continue reading “Boston Radio Pirate Runs for Mayor”
FCC Grossly Overstates Anti-Pirate Activity
A paragraph in the FCC’s annual performance report for fiscal year 2012 suggests the agency is on the warpath against unlicensed broadcasters:
The FCC shut down hundreds of pirate broadcast operations, which threaten the integrity of the nation’s communications infrastructure and caused interference to licensed broadcasters, air traffic control frequencies, and other public safety communications. There were $289,000 in penalties and 583 warnings issued during FY 2012.
Specious claims of the pirate threat aside, these numbers were quickly parroted by the Clear Channel-owned trade publication Inside Radio as evidence of a "pirate crackdown confirmed." But there’s no data to back up these claims. Continue reading “FCC Grossly Overstates Anti-Pirate Activity”
FCC Enforcement in 2012: Going Nowhere Fast
After plummeting in 2011, FCC enforcement against unlicensed broadcasting rebounded ever so slightly last year – but not in any meaningful fashion.
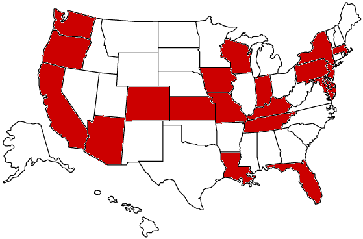 About 100 pirate radio stations in 19 states had contact with the federales in 2012, resulting in 245 specific enforcement actions. Interestingly, the vast majority of these happened in the first half of the year; for some reason, enforcement activity took a nosedive in July and never recovered. Continue reading “FCC Enforcement in 2012: Going Nowhere Fast”
About 100 pirate radio stations in 19 states had contact with the federales in 2012, resulting in 245 specific enforcement actions. Interestingly, the vast majority of these happened in the first half of the year; for some reason, enforcement activity took a nosedive in July and never recovered. Continue reading “FCC Enforcement in 2012: Going Nowhere Fast”
Larry Bloch: 1953-2012
Larry Bloch, a founding member of radio free brattleboro, died last month of pancreatic cancer. He was 59.
Bloch was one of those rare and lucky folks for whom activism was a full-time vocation. After working with Greenpeace throughout the 1980s, he created the Wetlands Preserve in New York City in 1989. The nightclub became a magnet for many bands that rose to fame out of the “alternative” music soup of the 1990s. Continue reading “Larry Bloch: 1953-2012”
Human Rights Radio Turns 25
 On November 26, 1987, Mbanna Kantako founded WTRA, an unlicensed microradio station broadcasting from the John Jay Homes in Springfield, Illinois.
On November 26, 1987, Mbanna Kantako founded WTRA, an unlicensed microradio station broadcasting from the John Jay Homes in Springfield, Illinois.
Legally blind and in his twenties at the time, Kantako started the station to protest the imminent destruction of the housing project by the city and the pervasive police abuse that occurred there.
WTRA would later be re-named Human Rights Radio to reflect the Kantako family’s widening concern with issues of social injustice.
Occupy the Airwaves
Two decades ago, thousands of people took to the air without permission from the FCC to protest the agency’s draconian policies regarding access to the airwaves. The microradio movement conducted a campaign of electronic civil disobedience, demonstrating that there was plenty of space on the dial for community radio while illustrating just how enriching local access to the airwaves can be. The end result of this campaign was the creation of the LPFM service.
Today, more than 10 years on from LPFM’s inception, unlicensed broadcasting remains alive and well, although the act is not as explicitly politicized as it once was.
This could change. Continue reading “Occupy the Airwaves”
The History of LPFM
What is LPFM?
LPFM stands for Low Power FM radio broadcasting. In the United States, the lowest minimum wattage a licensed FM radio station may have is 100 watts. There are lower-power FM transmitters in use, though, by some stations who want to increase their coverage area by extending their signal. These are called translators or boosters.
While these may only have a wattage measured in a range from dozens to hundreds, they are not true broadcast stations by the FCC’s definitions – they do not originate their own programming. They rely on a “parent” station to provide what they air.
Ham (amateur) radio uses a similar system called a repeater; people don’t broadcast from it. They shoot a signal into it, and then it gets re-broadcast to an area larger than what ham operators might reach with their own gear. In a nutshell, translators and boosters are the repeaters of FM radio.
LPFM is the common term used to define an FM broadcast station that originates its own programming but has the power of a translator or booster. Under current FCC rules, operating such a station is simply not allowed. You may also see LPFM referred to by other terms – like “LPRS,” “microradio,” and “mini-FM,” but they all mean the same thing. Continue reading “The History of LPFM”
Making Waves on Verge of Larger Distribution
Michael Lahey, the maker of what most likely is the best documentary yet-produced on the modern microradio/LPFM movement, Making Waves, has announced that the film is now available for free viewing online at Fancast (ironically, a Comcast-owned outlet).
In addition, Lahey says there’s a good chance that Netflix will pick up distribution of the documentary. Here’s how he says we can all help going about making that happen: Continue reading “Making Waves on Verge of Larger Distribution”
Scene Report: California
Skidmark Bob e-mailed recently to let me know that Freak Radio Santa Cruz is hunting for a new broadcast-home (yet again). The FCC dropped a warning-letter on the owner of the property hosting the station’s transmitter (a common tactic that’s gained popularity in recent years), who was duly unnerved and prompted the box to travel.
In spite of last year’s schism, the station appears to be on strong footing and Bob’s confident they’ll have a spot post-haste. Given that Freak Radio long separated its studio from transmitter, the comfy digs remain intact, and the station’s still streaming online. Continue reading “Scene Report: California”