Notes Mediageek, via the documentary’s distributor, B-Side Films. B-Side’s website is currently undergoing a major overhaul/redesign which may impact access, which will not be free. Back when Pirate Radio USA was in post-production Paul did an excellent extended interview with its producers that gives the film some extra context. Continue reading “Pirate Radio USA Available Online”
Month: May 2007
FCC Enforcement On Record Pace, Again
A long-overdue update to the Enforcement Action Database reveals that the FCC’s conducted more than 130 enforcement actions against pirate stations this year – nearly apace for all of 2005, when the FCC first began taking an administratively tougher stance on unlicensed broadcasting in a post-LPFM world. If this rate of activity stays constant the year could very well end on the north side of 400 enforcement actions.
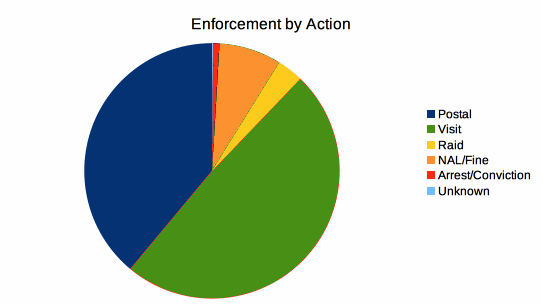 I call the FCC’s posture on pirate radio “administratively tougher” because, as the raw data shows, the agency has a hard time escalating its enforcement protocol. The duration between initial site-visit and follow-up warning letter is now in the 10-day range. Sometimes the period between a warning letter and fine can be as short as a month. Continue reading “FCC Enforcement On Record Pace, Again”
I call the FCC’s posture on pirate radio “administratively tougher” because, as the raw data shows, the agency has a hard time escalating its enforcement protocol. The duration between initial site-visit and follow-up warning letter is now in the 10-day range. Sometimes the period between a warning letter and fine can be as short as a month. Continue reading “FCC Enforcement On Record Pace, Again”
XM Repeater Network Entirely Pirate
Last October it was first disclosed that many of the terrestrial repeater stations used to boost the coverage footprint of the XM satellite radio network were operating without FCC approval. Recently XM filed a document with the Securities and Exchange Commission which seems to suggest the pirate nature of the network is more egregious than first confessed. Up to one-third of the company’s 800 repeater-stations are either placed in locations not approved by the FCC, operating at power levels well above those approved by the FCC, and several are on the air without FCC approval for their placement at all. The scope of such flaunting of the rules is unheard of: some of these illicit repeaters are operating with more than 40 kilowatts of power.
What’s more, it’s clear that XM had an economic incentive to break the law: the majority of its illicit repeaters serve the largest markets. More than half of those placed in the Los Angeles market, for example, are operating “at variance” from what they were authorized for. As a whole, according to XM’s own estimation, the 200+ rogue repeaters serve approximately 42 percent of its network’s total coverage footprint. Continue reading “XM Repeater Network Entirely Pirate”